
Cystoscopes
Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. The cystoscope has lenses like a telescope or microscope.
There are two main types of cystoscopy—flexible and rigid—differing in the flexibility of the cystoscope. Flexible cystoscopy is carried out with local anaesthesia on both sexes.
Laparoscopes
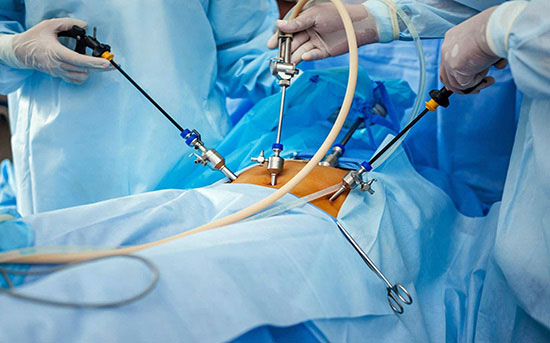
Laparoscopy is a type of surgery that uses smaller cuts than you might expect.
The process takes its name from the laparoscope, a slender tool that has a tiny video camera and light on the end. When a surgeon inserts it through a small cut and into your body, they can look at a video monitor and see what’s happening inside you. Without those tools, they’d have to make a much larger opening. Thanks to special instruments, your surgeon won’t have to reach into your body, either. That also means less cutting.

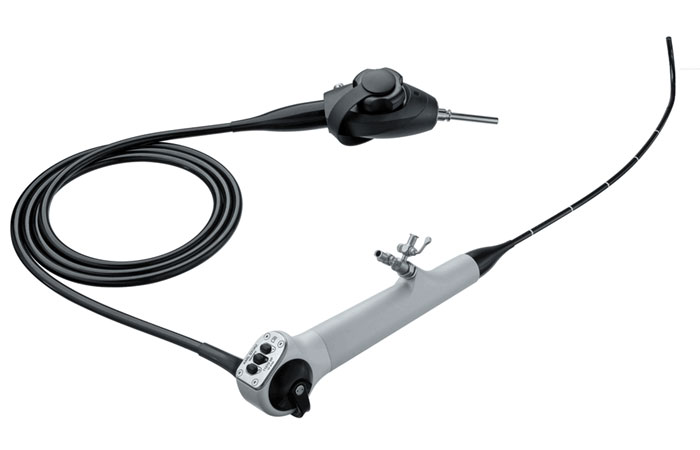
Semi-Flexible Mini Endoscope
A flexible endoscope is like a Swiss Army knife that is brilliantly designed into a compact device that includes a suction channel, light and image guides, irrigation channels, and biopsy channels capable of passing instruments through. The first major component within a flexible endoscope is the control body.
The basic design of most flexible endoscopes consists of a light guide connector, umbilical or universal cord, control body, insertion tube with internal channels, and the bending section which houses the several important components.
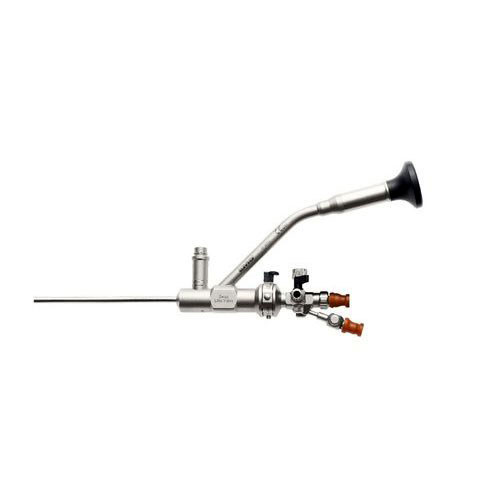
Nephroscope
The rigid nephroscope is an optical instrument which allows one to inspect the renal cavitary system and to perform different therapeutic procedures under direct visual control.
Commonly used rigid nephroscopes have diameters of up to 28 F that ensure maximal working channels and irrigation.
The 26 F standard instruments ensure a very good visibility, allowing the use of a wide range of rigid accessories. Also, continuous irrigation through the endoscope has a flow sufficient for maintaining the pyelocaliceal system distended during the procedure.


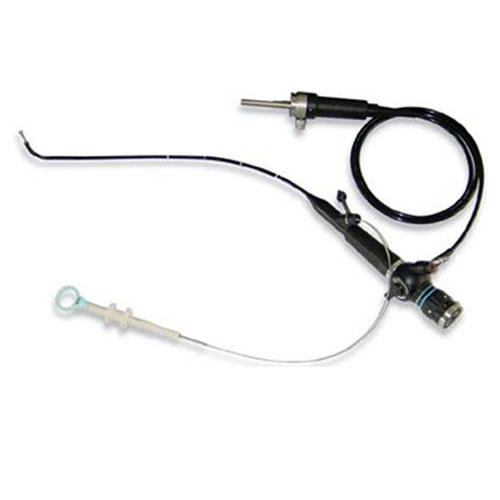
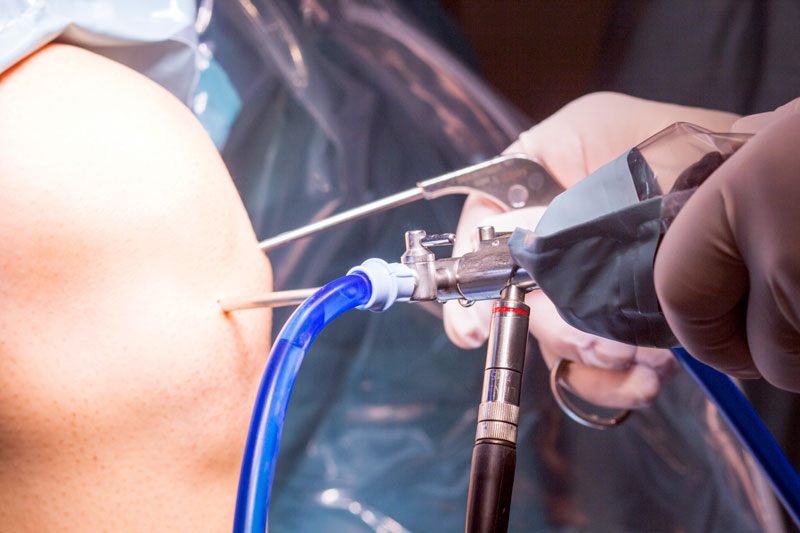
Uretero Renoscopes
Uretero Renoscope offered finds application in transurethral examination as well as treatment of ureter and renal pelvis. Coming with small outer sheath size of 8.5 Fr., these provide for optimal access to all renal areas and offers smooth control of distal tip, thus providing for direct transmission of hand movements through to distal end.
Offering superior picture quality because of continuous irrigation, it has separate working channel for laser fibres and delivers maximum reduction in time because of simultaneous use of laser fibre and stone basket. With brake mechanism for locking instrument tip, its smaller outer diameter provides for less traumatic experience for patients and provides for maximum stability.
Naso - pharyngoscopy
Naso - pharyngoscopy is also called nasopharynx endoscopy. It is a diagnostic medical procedure that involves the examination of the internal structures of the nose and throat (nasopharynx) to detect and diagnose abnormalities in the nasopharyngeal area.
A thin, flexible instrument called a nasopharyngoscope is inserted into the nose and throat through the nostrils. The scope has a camera and is connected to a light source.

Arthroscope
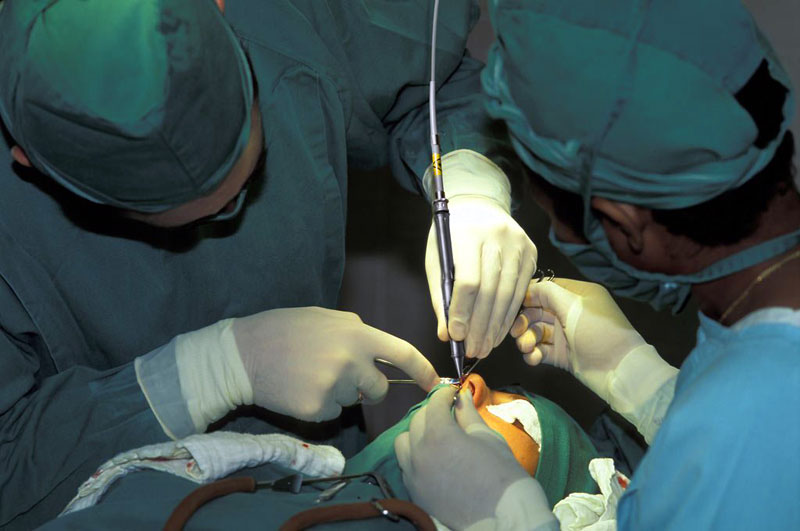
An Arthroscope is a small tube that is inserted into the body. It contains a system of lenses, a small video camera, and a light for viewing. The camera is connected to a monitoring system that lets a surgeon view the surgery while it is being done. The arthroscope is often used with other tools that are inserted through another cut or incision. These tools are used for grasping, cutting, and probing.
Arthroscopy is a procedure used for joint conditions. Originally, arthroscopy was used mainly for planning a standard open surgery. But with new tools and advanced surgical methods, many conditions can also be treated using an arthroscope.
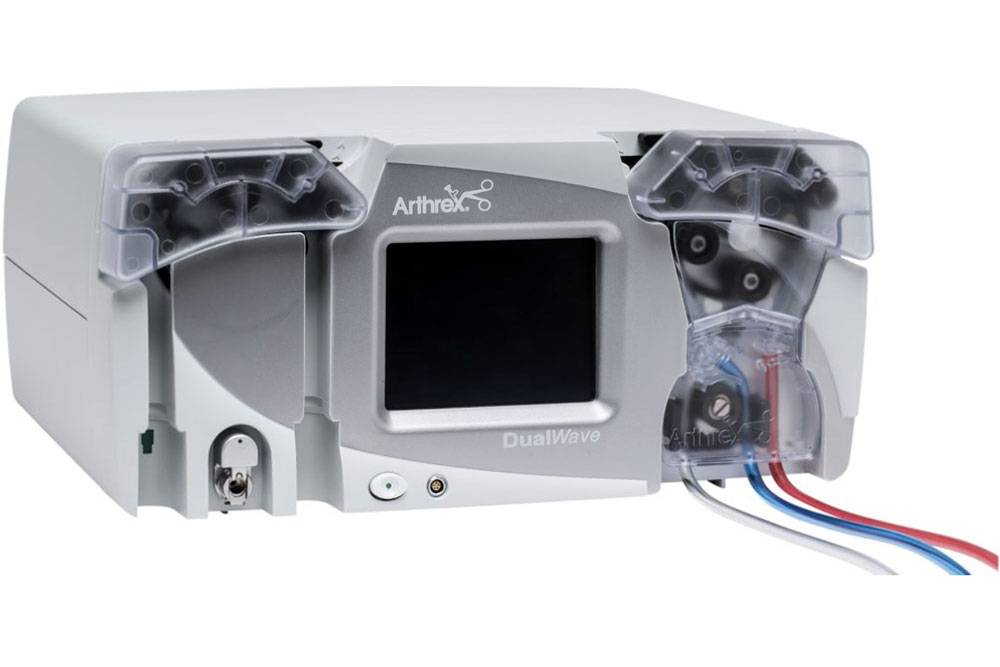
Arthroscopy with Pump
The use of an infusion pump is an effective method of irrigating the joint in arthroscopy. A Sarns roller blood pump is used to pump fluid into the joint through the arthroscope with outflow by gravity drainage through a plastic cannula. Flow and pressure can be adjusted independently.
Arthroscopy is a surgical procedure doctors use to look at, diagnose, and treat problems inside a joint. It's a minor surgery and is done on an outpatient basis, which means you can go home the same day.

Ent Surgery
Otolaryngology or ENT surgery focuses on surgically treating disorders of the ears, nose, and throat. This type of surgery is performed by an otolaryngologist, a doctor trained to treat patients with disorders and diseases of the ears, nose, throat, and other structures of the neck and face. ENT Surgical Procedures
- Ear tubes (tympanostomy)
- Myringoplasty
- Tympanoplasty
- Tympanoplasty with Ossicular Reconstruction.
- Tympanomastoidectomy.
- Tympanomastoidectomy with Ossicular Reconstruction.
- Stapedectomy.
Bronchofiber Scope
An endoscope for inspecting the interior of the tracheobronchial tree, either for diagnostic purposes (including biopsy) or for the removal of foreign bodies. There are two types: flexible and rigid.
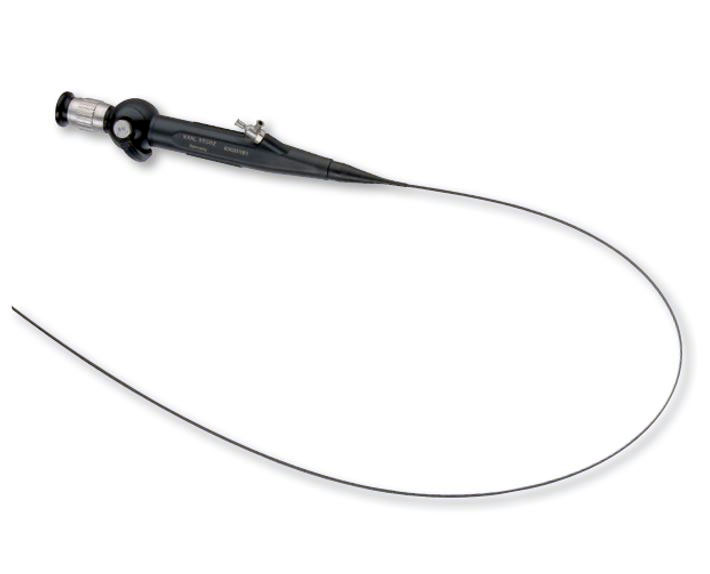
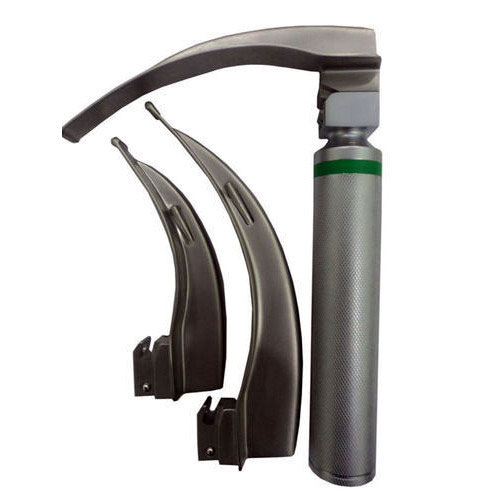


Laryngoscope
Laryngoscopy is a procedure a doctor uses to look at the larynx (voice box), including the vocal cords, as well as nearby structures like the back of the throat.
Laryngoscopes. The traditional laryngoscope is a device designed to assist in the visualization of the trachea during intubation. It consists of two parts: a handle with battery holder and a blade.
High Resolution Intubation Endoscope
PENTAX Medical’s proprietary Superfine fiber technology increases the number of optical fibers in the endoscope for better image resolution and color discrimination. It delivers bright, clear and high-resolution images supporting enhanced observation and precision during intubation.
Anaesthesia Machine
Healthcare India
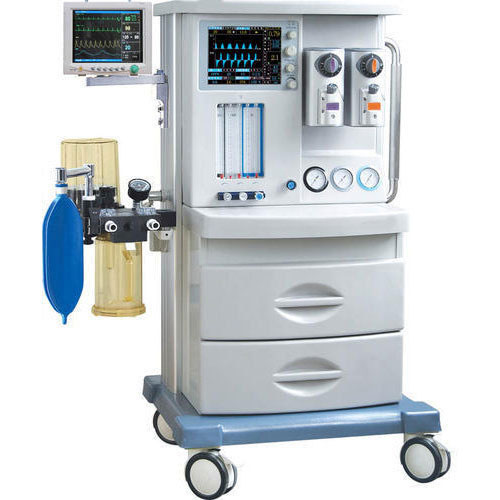
Work Station
The anaesthetic machine receives medical gases (oxygen, nitrous oxide, air) under pressure and accurately controls the flow of each gas individually. A gas mixture of the desired composition at a defined flow rate is created before a known concentration of an inhalational agent vapour is added.
Gas and vapour mixtures are continuously delivered to the common gas outlet of the machine, as fresh gas flow (FGF), and to the breathing sytem and patient
Accessories
They may also use ventilators and gas anesthesia devices. Anesthesiologists also work with medical, word processing, e-mail, and calendar and scheduling software.
- Pipeline inlets and pressure gauges.
- Ventilator power inlet.
- Oxygen pressure-failure device (fail-safe) and alarm.
- Flowmeter valves.
- Oxygen and nitrous oxide second-stage regulators.
- Oxygen flush valve.
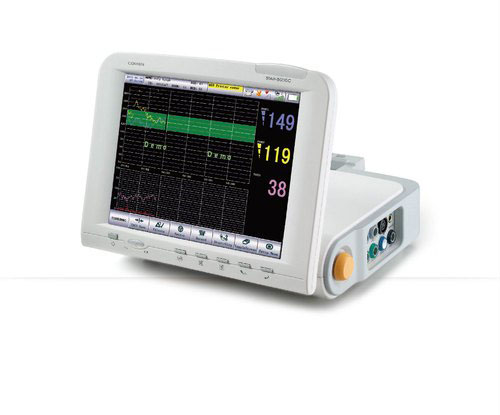
Fetal Monitor & Maternal Monitor
They are designed to measure, record, and display FHR, uterine contractions, and/or maternal blood pressure and heart rate before and during childbirth.
Fetal heart rate monitoring measures the heart rate and rhythm of your baby (fetus). This lets your healthcare provider see how your baby is doing. Your healthcare provider may do fetal heart monitoring during late pregnancy and labor. The average fetal heart rate is between 110 and 160 beats per minute.
Cardiology
Healthcare India
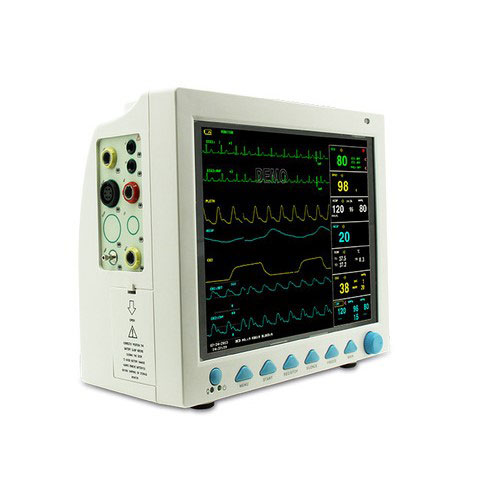

Multi Para Monitor
The multiparameter monitors are designed to give number of information on one screen and hence provides multiple information that is needed to understand the patient condition. It has emerged as a monitor to offer flexible solution for varying critical care need.
A multiparameter monitor is a medical device for monitoring a patient's vital signs. It is mainly used in intensive care, hospitalization or ER. In general, basic models are used to monitor cardiac activity (ECG), blood pressure (NIBP), respiration (RESP), oxygen saturation (SpO2) and temperature (TEMP).
ECG Machine - 3/6/12 CHANNEL
Channel – The other term commonly used in reference to ECG machine is number of 'channels'. ECG machines may come as single channel, 3-channel, 6-channel or 12-channel configurations. Each lead measurement done a. s detailed above is then passed through an 'amplifier' channel and recorded.
Uses 3 electrodes (RA, LA and LL) Monitor displays the bipolar leads (I, II and III) To get best results – Place electrodes on the chest wall equidistant from the heart (rather than the specific limbs)
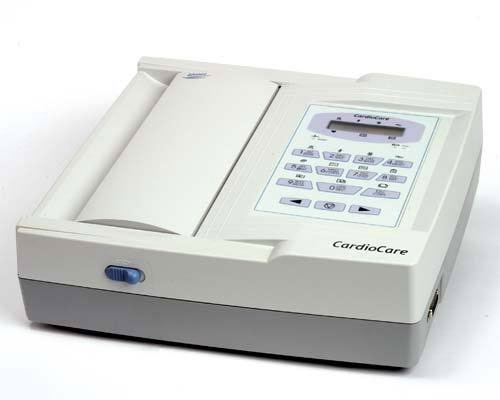

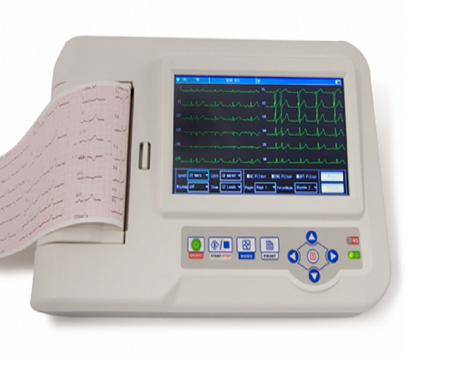
6 & 12 Chanel ECG with Interpretation
Heart signals are generated by the body and have amplitudes of a few millivolts. Specific electrode locations allow the electrical activity of the heart to be viewed from different angles, each of which is displayed as a channel in the ECG printout.
The normal range of the ECG differed between men and women: heart rate 49 to 100 bpm vs. 55 to 108 bpm, P wave duration 81 to 130 ms vs. 84 to 130 ms, PR interval 119 to 210 ms vs. 120 to 202 ms, QRS duration 74 to 110 ms vs.
Critical Care
Healthcare India
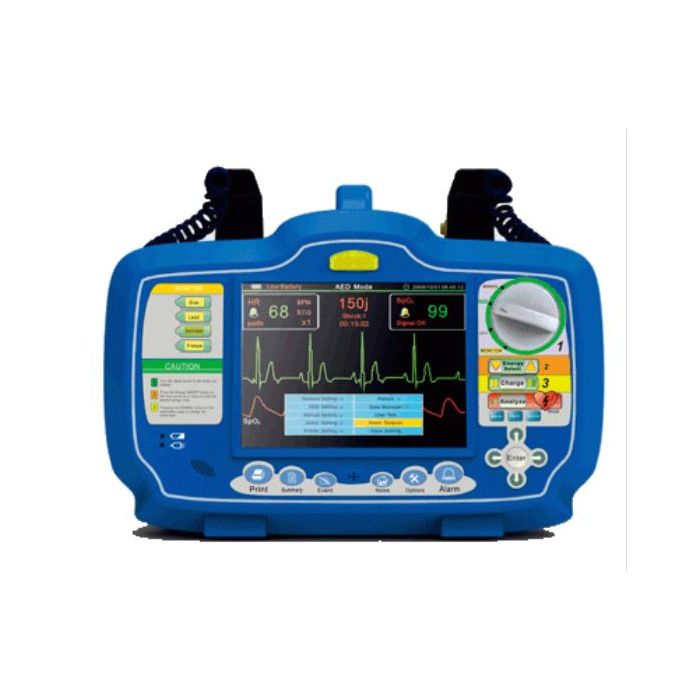
Automatic External Defibrillator & Defibrillator with Monitor
Automated external defibrillators (AEDs) are portable, life-saving devices designed to treat people experiencing sudden cardiac arrest, a medical condition in which the heart stops beating suddenly and unexpectedly.
The combination of CPR and early defibrillation is effective in saving lives when used in the first few minutes following collapse from sudden cardiac arrest.
Syringe Pump
Syringe pumps are used to deliver a very small amount of medications, mechanically moving the piston of a syringe to send medication into IV tubing.
A syringe driver, also known as a syringe pump, is a small infusion pump, used to gradually administer small amounts of fluid (with or without medication) to a patient or for use in chemical and biomedical research.
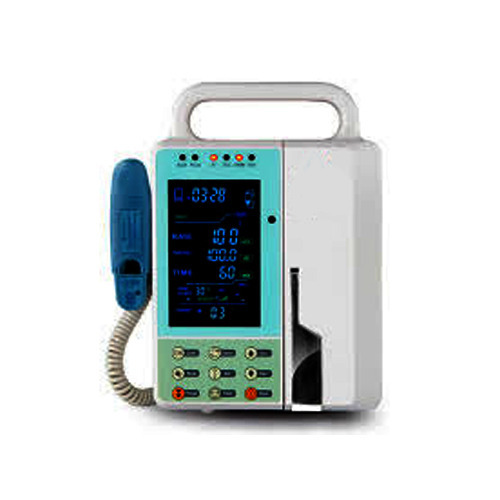

Volumetric Infusion Pump
Volumetric infusion pumps (VIP) are medical devices capable of delivering continuous and very specific amounts of fluids at very slow to very fast rates. Infusion pumps are commonly used to control the flow of intravascular drugs, fluids, whole blood, and blood products to patients.
Plastic tubing is connected to a bag of intravenous fluids, which is threaded through the volumetric infusion pump; this tubing is connected to the patient via intravenous access. These pumps are programmed by the nurse to deliver medications to a patient at a specific or titrated rate according to the doctor's orders.